Nginx Memcached module And PHP
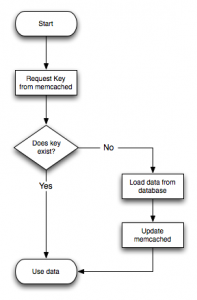
I’ve seen lots of tutorials on internet explaining how set nginx to use memcached module. But, i’ve rarely seen them explaining, even the easiest one on how to populate memcached with data generated by php. When i’m getting in touch with memcached for the first time, i thought default configuration like this will be working out of the box. without touching php script. 😀
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
# ...
location ~ \.php$ {
set $memcached_key "kutu:$request_uri";
memcached_pass 127.0.0.1:11211;
default_type text/html;
error_page 404 405 502 = @cache_miss;
}
location @cache_miss {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /path/to/yoursite/htdocs$fastcgi_script_name;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
}
# ...
}
Well, i was totally confused :D. so, to prevent other people misinterpret on how nginx memcached module works, i wrote simple examples, and simple explainations on how to configure nginx and populate data generated from php.